Quantum Computers: Future of computing, Really ??

"The massive amount of processing power generated by computer manufacturers has not yet been able to quench our thirst for speed and computing capacity. Will we ever have the amount of computing power we need or want? If, as Moore's Law states, the number of transistors on a microprocessor continues to double every 18 months, the year 2020 or 2030 will find the circuits on a microprocessor measured on an atomic scale. And the logical next step will be to create quantum computers, which will harness the power of atoms and molecules to perform memory and processing tasks. Quantum computers have the potential to perform certain calculations significantly faster than any silicon-based computer."
What is a quantum computer?
From Wikipedia, A quantum computer is one which uses quantum states of subatomic particles to store and process information. In layman's terms, a machine which uses quantum effects of atomic particles to process data can be termed as a quantum computer.
How does it Work?
 A classical computer performs operations using classical bits which could be zero or one, in contrast, a quantum computer uses something called quantum bits or qubits which can be zero and one simultaneously which provides it supremacy over classical computers.
A classical computer performs operations using classical bits which could be zero or one, in contrast, a quantum computer uses something called quantum bits or qubits which can be zero and one simultaneously which provides it supremacy over classical computers.
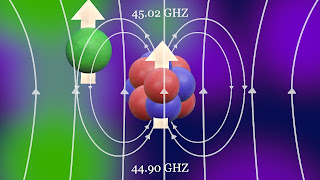
There are a number of components which can be used as a quantum bit, a single photon a nucleus and an electron as well. The most common example is the use of an electron of phosphorus as a quantum bit.
All electrons have their magnetic fields so they can be thought as a bar magnet which, when exposed to external magnetic fields can align according to that external magnetic field, just like a compass needle aligns with the magnetic field of the earth. In its lowest state called as spin down state or zero state By providing some energy, they can be rotated to spin up state or one state. these two state are equivalent to zero and one of classical bits. But here's the funny part they can be both zero and one at a time, partially by virtue of a quantum property called quantum superposition. "The difference between classical bits and qubits is that we can also prepare qubits in a quantum superposition of 0 and 1 and create nontrivial correlated states of a number of qubits, so-called 'entangled states'."
 All the processing is done in this superposition state, special algorithms are designed to solve a certain type of problem. Although quantum bits can be super positioned into infinite states , we need to align them to base states while measuring and all the information before conversion to these states is lost. Because we cannot measure superposition. We want to design logic operations to convert these superpositions into basic levels. The amount of equivalent classical bit information contained by n quantum bits is 2^n . So a quantum computer becomes exponentially fast compared to a classical computer in certain type of applications.
All the processing is done in this superposition state, special algorithms are designed to solve a certain type of problem. Although quantum bits can be super positioned into infinite states , we need to align them to base states while measuring and all the information before conversion to these states is lost. Because we cannot measure superposition. We want to design logic operations to convert these superpositions into basic levels. The amount of equivalent classical bit information contained by n quantum bits is 2^n . So a quantum computer becomes exponentially fast compared to a classical computer in certain type of applications.Will it replace classical computers in Future?
Simple word answer is NO. A quantum computer is faster than a classical computer for only certain type of operations e.g in solving algorithms to forecast weather. Day to day tasks of a common consumer like watching videos and playing games is not going to have any significant boost in performance when computed with quantum computers. classical computers. It's not like they are always fast, it's just logical operations to reach the result is exponentially small. The improvement is not in the speed of operations, it's in the number of operations needed to reach the result.
Limitations of quantum computing
Current approaches to quantum computation exploit the phenomena of entanglement and superposition to create a paradigm that is more powerful than that of classical computing. The field has grown from the exotic arena confined to a few theoretical physicists into a full scale theoretical and experimental research area with millions of dollars being spent to build prototypes of quantum computers. Many believe that these computers are the only way that one can transcend the eventual limitations of Moore’s law, where currently advances have been obtained mainly by advances in lithography. The requirements for physical implementation of a quantum computer include a well defined extendible qubit array for stable memory, feasible state preparation for the initial state, long decoherence time, a universal set of gate operations and capability for singlequantum measurements Not all these requirements are currently unconditionally achievable.
1. Sensitivity to interaction with environment
Quantum computers are extremely sensitive to interaction with the surroundings since any interaction (or measurement) leads to a collapse of the state function. This phenomenon is called decoherence. It is extremely difficult to isolate a quantum system, especially an engineered one for a computation, without it getting entangled with the environment. The larger the number of qubits the harder is it to maintain the coherence. In a recent review, H.D. Zeh argues that decoherence cannot be reversed by redundancy coding. This leads to the important consequence that decoherence in quantum computers cannot be error-corrected for in the usual manner by means of redundant information storage. Adding extra physical quantum bits to achieve redundancy, as it would be appropriate to correct spin or phase flips in the system, would in general even raise the quantum computer’s vulnerability against decoherence – for the same reason as the increased size of an object normally strengthens its classicality.
In another paper, the influence of spontaneous symmetry breaking on the decoherence of a many-particle quantum system was studied and it was shown that this symmetry breaking imposes a fundamental limit to the time that a system can stay quantum coherent. Miniaturization of the systems seems to lower the time limit. This means that the decoherence constraints on quantum computing are even more severe than thought before.
 The main problem with quantum computing is to actually develop it as a personal computer, and hopefully they will be in the price range of every day consumers. It will be comparable to when computers were first introduced. They were the size of a room and were very costly. Then they kept getting smaller and smaller and eventually appeared on the market. Most likely, the same sort of transition from those computers to quantum computers will take place, at first they will be accessible only to big businesses but then they will go on the commercial market. The main people that will lose out because of quantum computing are the companies who did not learn the lesson of history. This refers to the companies that did not invest in computers and stuck with punch card and tabulating technology because they did not believe that computers would become so popular, and these companies went out of business. An example of a company that did invest is IBM, and they are one of leading computer manufacturers nowadays, who (you guessed it) are already investing in quantum technology.
The main problem with quantum computing is to actually develop it as a personal computer, and hopefully they will be in the price range of every day consumers. It will be comparable to when computers were first introduced. They were the size of a room and were very costly. Then they kept getting smaller and smaller and eventually appeared on the market. Most likely, the same sort of transition from those computers to quantum computers will take place, at first they will be accessible only to big businesses but then they will go on the commercial market. The main people that will lose out because of quantum computing are the companies who did not learn the lesson of history. This refers to the companies that did not invest in computers and stuck with punch card and tabulating technology because they did not believe that computers would become so popular, and these companies went out of business. An example of a company that did invest is IBM, and they are one of leading computer manufacturers nowadays, who (you guessed it) are already investing in quantum technology.The Future of Computing
“This quantum bit is more versatile and more long-lived than the electron alone, and will allow us to build more reliable quantum computers” . Furthermore, by building on silicon technology, this development makes it possible to build quantum computers using existing fabrication processes used today. It’s a stable future for quantum computing.
Described as the 21st century’s space race, developing better quantum computers opens the door to faster and more efficient computing that will greatly improve various industries, from finance and healthcare to security and defense. Quantum computers can also greatly improve the performance of existing artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
" Quantum computing is future of computing technology, even though they are not that efficient in day to day tasks of a regular consumers and it will take long before we see quantum computing in personal computers. But that can't deny the fact that quantum computing is going to change the way of computing and will extend their limits beyond our imagination"
"If you liked the content then like my facebook page and subscribe to my blog's newsletter"






Comments
Post a Comment